What is the MAC address?
The MAC address (Medium Access Control address) is a unique network address for each Network Interface Controller to identify the hardware on the network segment. The address is generally expressed as six hexadecimal digits, sometimes separated by a '-', ':', or without a separator.
The MAC address is assigned by the hardware manufacturer during production, however many network controllers allow the operating system (via the drivers) to override the MAC address, this is handled at the operating system level and does not change the address stored in the adapter.
The first three octets (first three hexadecimal values, six characters) identify the network hardware manufacturer while the last three octets should be unique within each hardware manufacturer's product line. For example Plugable's MAC addresses all begin with "8CAE4C", with lower values typically representing older companies, "000000" belongs to Xerox for example, some companies have multiple ranges of MAC addresses.
Why it can be useful to override the manufacturer's address?
Setting a custom MAC address can provide anonymity when connecting to public networks. It can also be used by an IT Network Administrator to provide specific access rights to computers based on the connection.
It can also be useful for Network Administrators for testing, troubleshooting, and maintenance to simulate different devices without having access to that specific device.
Changing the Mac Address in Windows
The MAC address can be manually set from the Device Manager:
1. Right-click on the Start Menu and select Device Manager from the pop-up window
2. Expand the Network adapters section and double-click on the network adapter to be modified
3. From the network adapter properties pop-up window, select the Advanced tab
4. Under the Property: category, scroll down to and select "Network Address"
5. In the Value: field, enter the new MAC Address in hexadecimal format, the field has a maximum of 12 characters so do not use any separators between octets
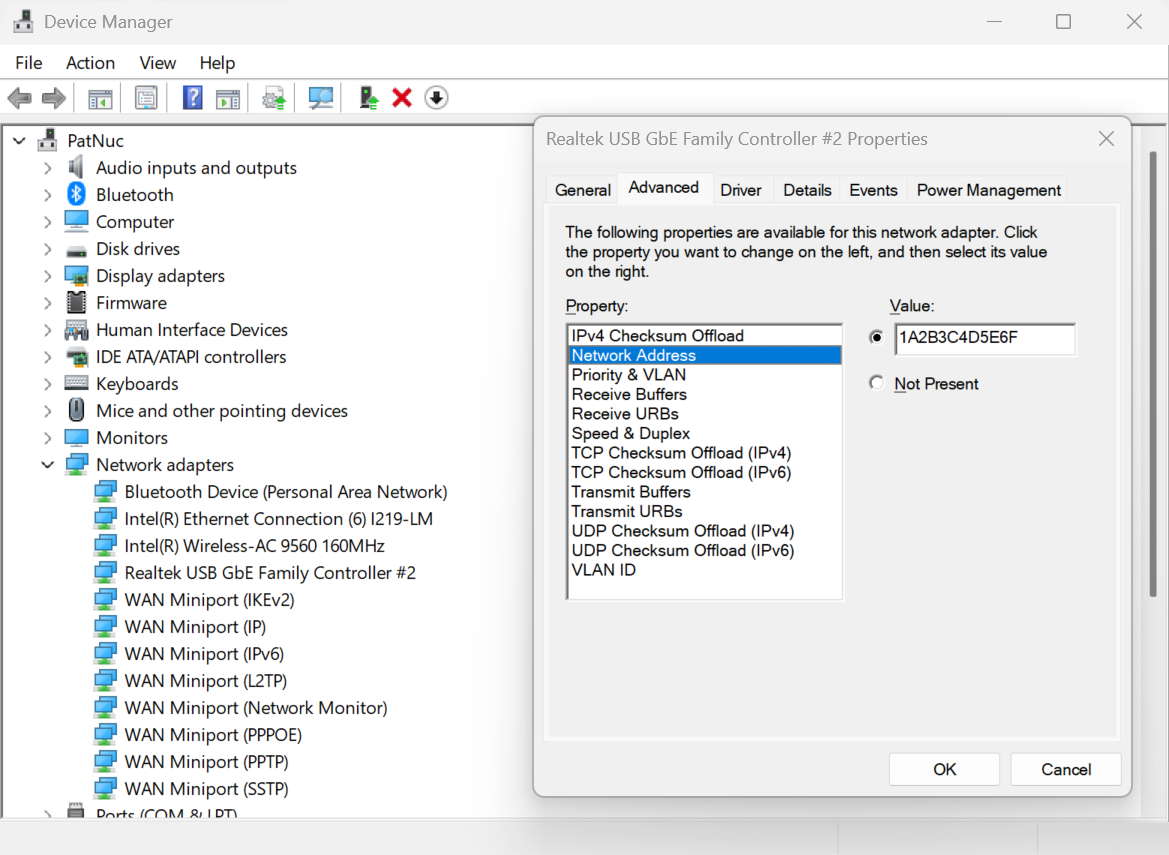
6. Select the OK button to proceed
You can also check the MAC Address from the command line
1. Right-click on the Start Menu and select Terminal or Windows PowerShell
2. Type in the following command ipconfig /all or ipconfig /all | findstr C:/"Physical Address" to filter just the Physical Address lines.
3. Scroll through the output to find the target network adapter and Physical Address

